Bubble detection by using openCV
Motivation
My colleagues are working on bubbly flows and the would like to detect bubble from a static image like the following one.
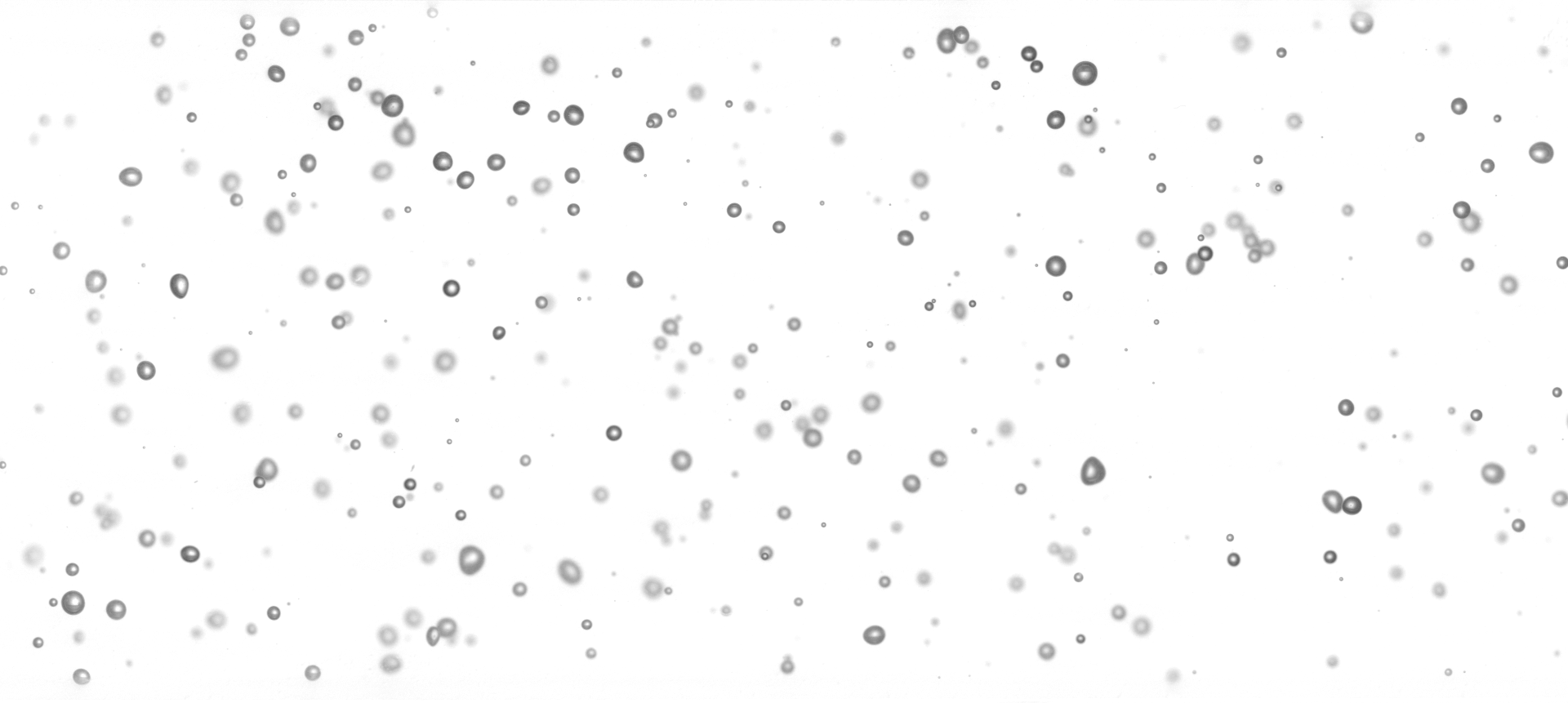
They want to know the center coordinate of each bubble in the image and its radius (assuming the bubbles are circles). They have thousands of similar images waiting to be processed and there must be an automated way to perform the task. I am recently working with the OpenCV package which has almost everything needed off the shelf. So I just wrote a short script to do the job.
Procedures
-
The script reads an image from the file system, shows it in an OpenCV window.
-
The image is converted into gray-scale and blurred.
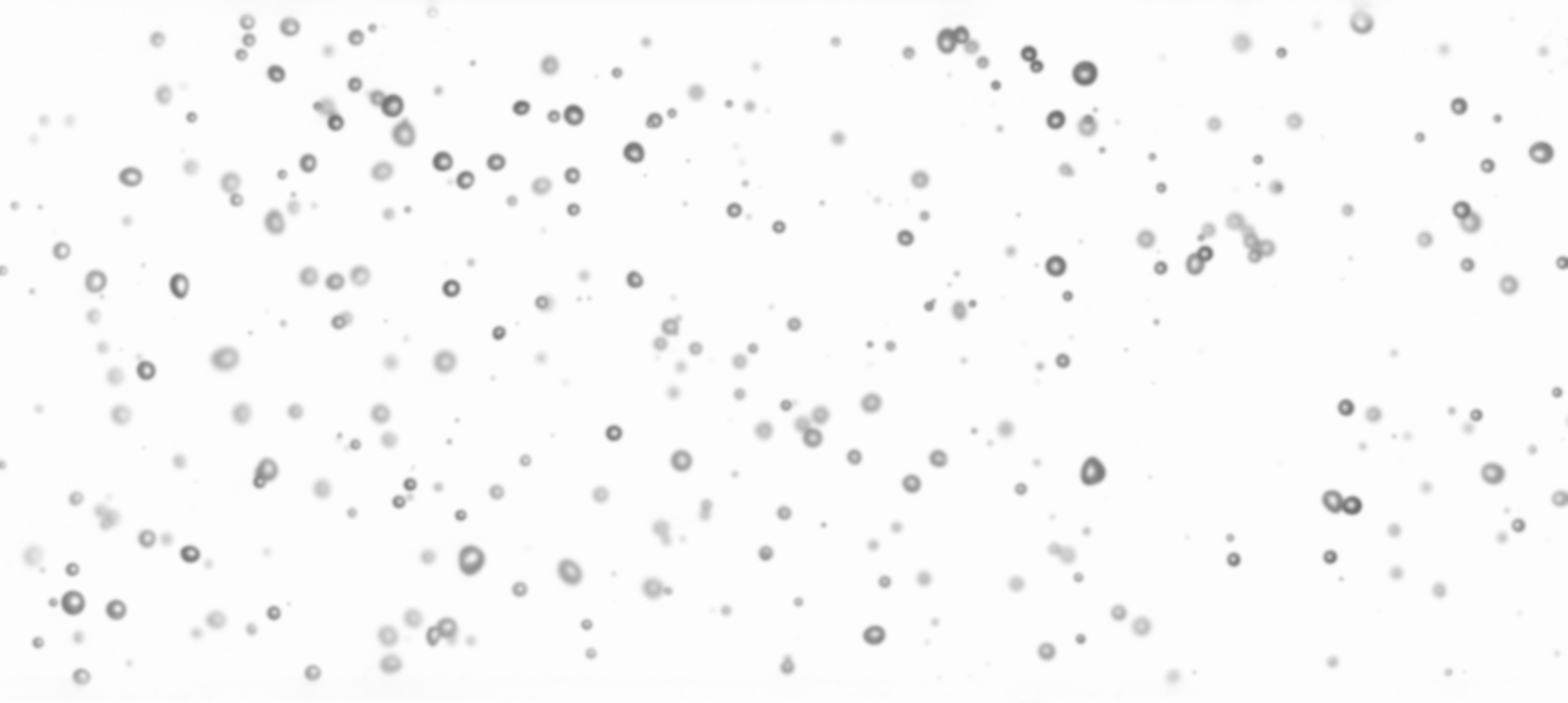
- The image is further processed such that the “holes” are filled with solid color.
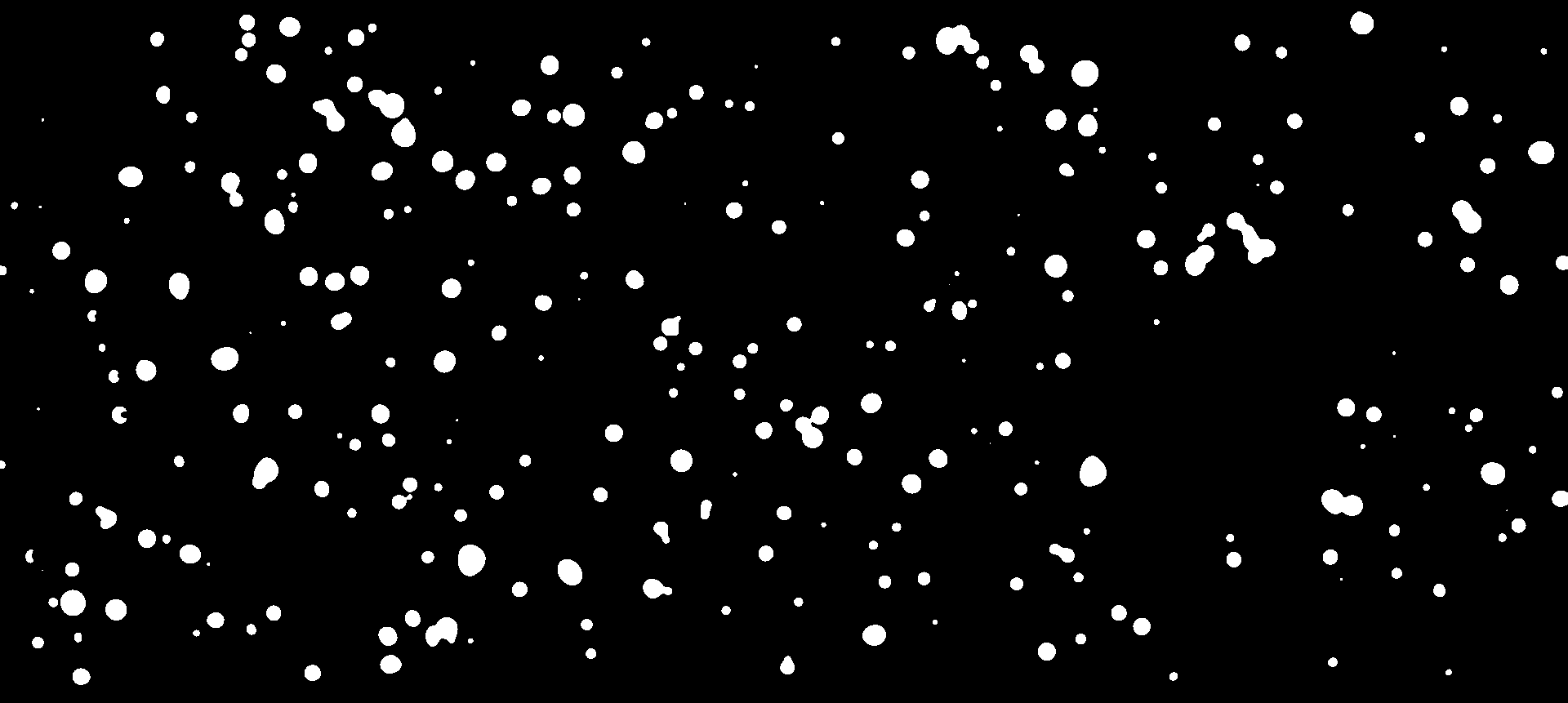

-
The Hough transformation implemented by OpenCV is then used to detect circle patterns
-
Re-draw the original image with detected circles colored in green.
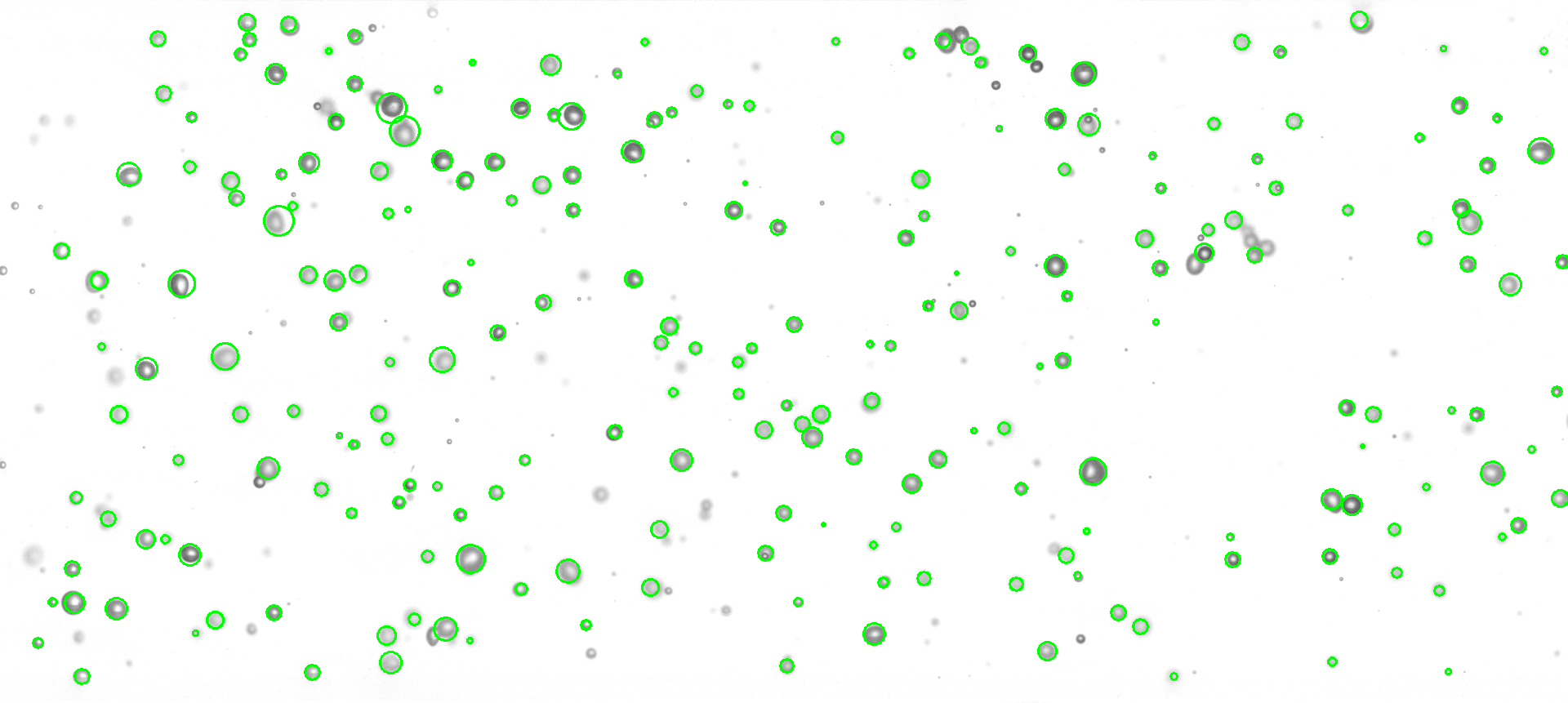
OpenCV does a pretty good job if the parameters are set properly.
Acknowledgment
The original image is provided by my colleague, Yuchen Song (songyuchen@sjtu.edu.cn).
The source code
The code is written in Python with cv2 and has been tested with Python2 and Python3.
import numpy as np
import argparse
import cv2
def fill_holes(imInput, threshold):
"""
The method used in this function is found from
https://www.learnopencv.com/filling-holes-in-an-image-using-opencv-python-c/
"""
# Threshold.
th, thImg = cv2.threshold(imInput, threshold, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
# Copy the thresholded image.
imFloodfill = thImg.copy()
# Get the mask.
h, w = thImg.shape[:2]
mask = np.zeros((h+2, w+2), np.uint8)
# Floodfill from point (0, 0).
cv2.floodFill(imFloodfill, mask, (0,0), 255)
# Invert the floodfilled image.
imFloodfillInv = cv2.bitwise_not(imFloodfill)
# Combine the two images.
imOut = thImg | imFloodfillInv
return imOut
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Extract arguments from the command line.
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
ap.add_argument("-i", "--image", required = True, help = "Path to the image.")
args = vars(ap.parse_args())
# Load the image.
image = cv2.imread(args["image"])
cv2.imshow("Original image", image)
# Convert the image into grayscale image.
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
blurred = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (11, 11), 0)
cv2.imshow("Blurred", blurred)
# Fille the "holes" on the image.
filled = fill_holes(blurred, 220)
cv2.imshow("Filled", filled)
# Find circles by the Hough transfermation.
circles = cv2.HoughCircles(filled, cv2.HOUGH_GRADIENT, 1, 20, param1 = 25, param2 = 10, minRadius = 0, maxRadius = 20)
# Draw circles on the original image.
if circles is not None:
for i in range(circles.shape[1]):
c = circles[0, i]
cv2.circle( image, (c[0], c[1]), c[2], (0, 255, 0), 2)
print("i = %d, r = %f" % (i, c[2]))
cv2.imshow("Marked", image)
else:
print("circle is None")
# Block the execution.
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()